The Estimates Committee of India (ECI) is a parliamentary committee that was first constituted in 1921. After independence, the committee was reconstituted in 1950 on the recommendation of John Mathai.
It consists of 30 members, all drawn exclusively from the Lok Sabha and does not have representation from the Rajya Sabha. All parties are given due representation in the committee, and a minister cannot be elected as a member. The Speaker of the Lok Sabha elects the Chairman of the committee from among its members.
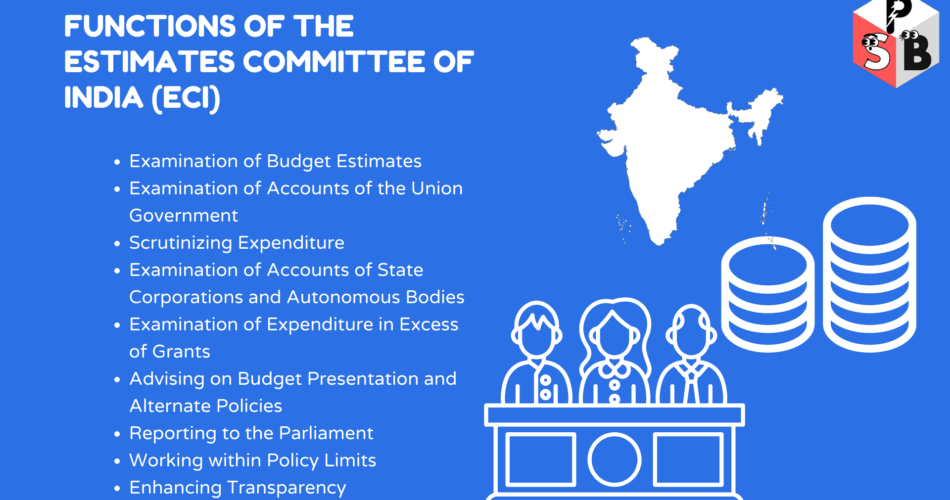
Functions of Estimates Committee of India (ECI)
The Estimates Committee of India performs several crucial functions that help ensure transparency and accountability in the utilization of public funds in the country.
The Functions of ECI are as follows –
- Examination of Budget Estimates
- Examination of Accounts of the Union Government
- Scrutinizing Expenditure
- Examination of Accounts of State Corporations and Autonomous Bodies
- Examination of Expenditure in Excess of Grants
- Advising on Budget Presentation and Alternate Policies
- Reporting to the Parliament
- Working within Policy Limits
- Enhancing Transparency
Here is a more detailed explanation of each of the functions of ECI:
1. Examination of Budget Estimates
One of the primary functions of the Estimates Committee is to examine the estimates included in the budget. The committee aims to report on the efficiency of the policy underlying the estimates presented to the President.
The committee examines the appropriation accounts and the finance accounts of the Union Government and any other accounts laid before the Lok Sabha.
The committee scrutinizes the appropriation accounts and the audit report of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) to ensure that the money disbursed was legally available for the applied service or purpose, that expenditure conforms to the authority that governs it, and that reappropriation has been made in accordance with the related rules.
2. Examination of Accounts of the Union Government
The committee examines the appropriation accounts and the finance accounts of the Union Government and any other accounts laid before the Lok Sabha. This examination helps the committee to assess the spending patterns and trends of the Union Government, identify areas for improvement, and make recommendations to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in the use of public funds.
3. Scrutinizing Expenditure
The Estimates Committee scrutinizes the appropriation accounts and the audit report of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) to ensure that the money disbursed was legally available for the intended service or purpose and that expenditure conforms to the authority that governs it.
The committee also reviews the audit report of the CAG to ensure that the money disbursed was well laid out within the limits of the policy implied in the estimates. This scrutiny helps to ensure that public funds are used in accordance with the provisions of the law and that they are utilized efficiently and effectively.
4. Examination of Accounts of State Corporations and Autonomous Bodies
The committee also examines the accounts of state corporations, trading concerns, and manufacturing projects, as well as the audit report of the CAG on these entities. It also examines the accounts of autonomous and semi-autonomous bodies, the audit of which is conducted by the CAG.
The committee examines money spent on services during a financial year in excess of the amount granted by the Lok Sabha. The committee is assisted in this function by the CAG.
5. Examination of Expenditure in Excess of Grants
The committee examines money spent on services during a financial year in excess of the amount granted by the Lok Sabha. This examination helps to ensure that public funds are used in accordance with the provisions of the law and that they are utilized efficiently and effectively. The committee may make recommendations to the Lok Sabha on how to better manage the utilization of public funds.
6. Advising on Budget Presentation and Alternate Policies
In the exercise of its functions, the committee also seeks to ensure that the money is well-laid out within the limits of the policy implied in the estimates. It also suggests the form in which estimates are to be presented in the Parliament and suggests alternate policies to enhance efficiency.
The committee continues its examination of the estimates throughout the financial year and reports to the Lok Sabha as its examination proceeds. The committee works within the limits of the policy approved by the Parliament.
7. Reporting to the Parliament
The Estimates Committee continues its examination of the estimates throughout the financial year and reports to the Lok Sabha as its examination proceeds. These reports provide the Parliament with valuable information on the utilization of public funds and help to ensure that the government is held accountable for its spending decisions.
8. Working within Policy Limits
The Estimates Committee works within the limits of the policy approved by the Parliament. This ensures that the committee operates within the bounds of the spending priorities and policy frameworks approved by the Parliament.
9. Enhancing Transparency
The functions of the Estimates Committee serve to enhance transparency in the workings of parliamentary democracy by ensuring that public funds are used efficiently and effectively and that the Parliament is informed of any issues related to the use of these funds. The committee’s examination of the budget, accounts, and expenditure of the Union Government, state corporations, and autonomous bodies